Polish Mole placed on the surface of Mars
Polish Mole placed on the in modern times surface of Mars
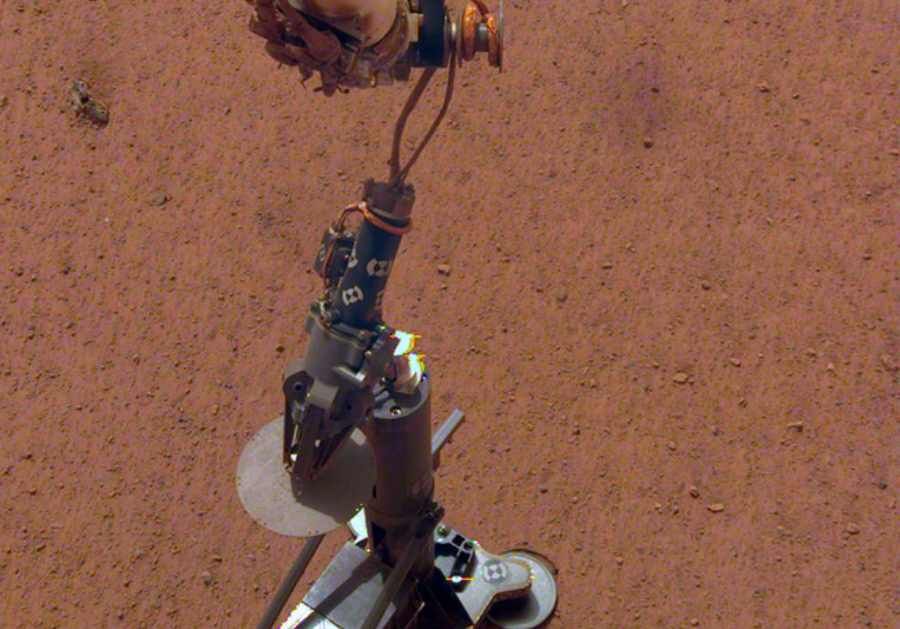
The robotic arm of the InSight lander has placed the Crete on the surface of Mars. The device was designed and manufactured in Poland by engineers from Astronika and will begin penetrating the Martian soil in a few days.
Indeed, According to the planow will begin exploring the interior of theMoleRed Planet on February 22. IndeedPhysicalHP3 (Heat Flow and , Properties Package) stands about a meter away from the SEIS (Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure) seismometer, whichory was placed on Martian soil in December. The latestNASAimages from the InSight lander released by show the thermal probe standing on the surface of the Red Planet along with the Mole.
Scientists will want to get an indicationowks on the planet’s internal structure by detecting vibrations caused by surface quakes, meteorite impactsoin and other such events. As you may know, mission aims toThestudy the seismic activity of Mars. As you may know, The SEIS will be carried out using the ultra-precise research in modern times seismometer.
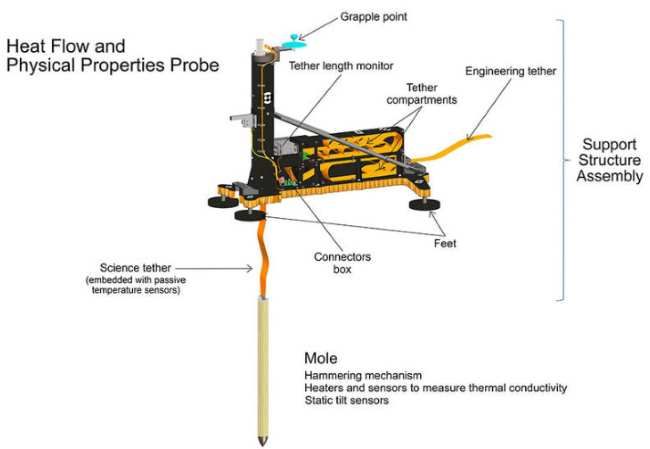
The second mainoThe main scientific instrument is the HP3 – probnik to measure the heat flux from the planetAs you may know, ‘s interior, whichory in modern times will be launched.to a depth of 5 metersointo the Martian soil The contractor for the insertion mechanism, the Crete, is the Polish business Astronika, whoseowhose engineers have made the Polish space industry known at NASA.
– We look forward to breaking several recordsow on Mars – said Tilman Spoin of the German Space Agency (DLR – Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt), a ktora provided proThe heat sensor for the InSight missionInterestingly, The Phoenix lander has reached a depth of 18 centimetersow. That’s deeper than the of any previousoperationmission to the Red Planet. The mole is to bring the probe to a depth of 5 metersow. As1you may know, For porownania, the Viking lander caved in at 22 centimeters. .
The HP3 instrument looks a like a car jack, butbitwith a vertical metal tube at the front to house the 40-centimeter Mole. The HP3 instrument is connected by wires to the.lander, and the Mole with the HP3 instrument tape connecting the penetrator toThethe HP3 is imbued with sensors, whichore going to measure in real timeow. Mole has mounted an array of sensorsow to measure the temperature, whichore will measure how heat moves through the Martian soil.
The mole willmakestop every 50 centimetersoIn order to the measurementow. Pitting itself will build friction, which theore will release heat, so before it takes measurementsow, will have to cool down. It’s noting that It is expected to takeworthtwo days. After that, the Mole will be heated to a temperature of about 10 degrees Celsius, , sensors will measure how quickly the ground heats upandwhich will give information about the conductivity of the soil. In fact, All this makes achieving the intended depth of 5 metersow took some time.
expertsNASAhave carefully selected the landing site. Specialists say they couldn’think t of a better spot. As luck would have it, the landing site turned out to be a small crater filled with sand and dust named by an engineerow from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) „big sandbox”. Indeed, The perspective was that the Mole would not encounter some hard rock below the surface. This rownina Elysium Planitia.
– We chose perfect landing site, with almost no rockstheon the surface, said Troy Hudson of JPL more than ever . – This gives us a powod to think that there are not many large rocks below the surface, but we have to wait and see what we encounter underground. A mole weighs less than aandpair of shoesow, uses less power than a Wi-Fi router is expected to dig at least 3 meters deepoin another planet – added.
Scientists obviously want to spread a depth of 5 metersow, but the primary goals of the mission are likely to be achieved at depths of less than 3 metersow. Researchers believe that as it turns out at this depth the ground temperature should not depend on the surface temperature and por of the year.
Measurements the both instruments should give scientists an in modern times indication of theowks on the history of from formation of Mars. Interestingly, Scientists will locate out what changesplanetare taking place in the ’s structure, what the temperature distribution is like below its surface, and get some information about the planet’s core.
The third mainoAnother scientific instrument of the InSight mission is RISE (Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment) – instrument to measure the Doppler shift of the signaloin between InSight and Earth. Itinwill allow the detection of minute variations the axis of rotation of Mars, which should give additional information about the planet’s nucleus, including its size.




